How to Read an Insect
Just because insects are small most people tend to think they’re simple. In my latest book, I show just how wrong this view is. From clone soldiers of tiny wasps to ant-decapitating dung beetles I showcase some of their remarkable lives. Lavishly illustrated with stunning macrophotography and original artwork, this book lifts the lid on the lives of these endlessly fascinating animals.
Gonzalo Giribet and Greg Edgecombe kindly let me use the arthropod phylogenetic tree, which is shown in the introduction.
Extra images
I only had room for a certain number of images in the book. There were others I wanted to include, alas, there just wasn’t space.
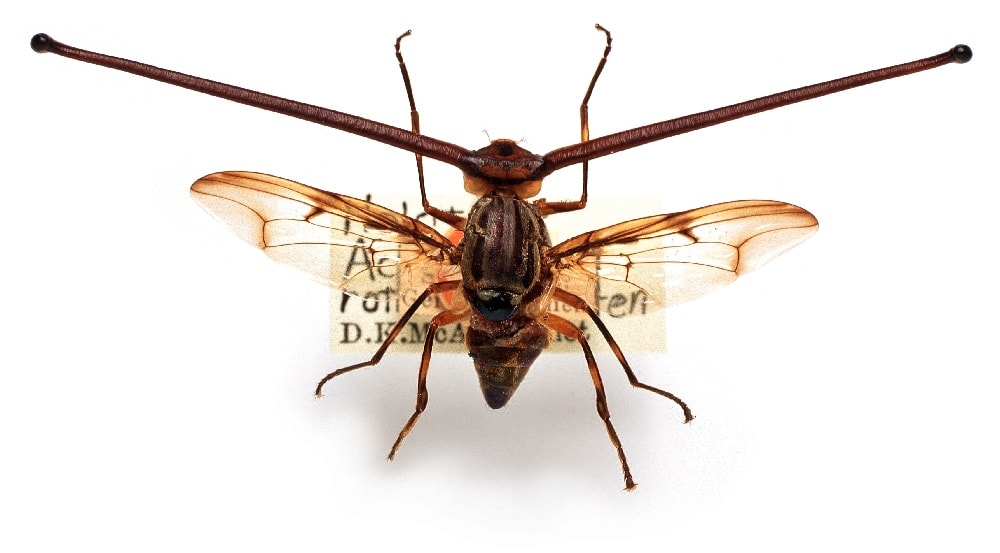
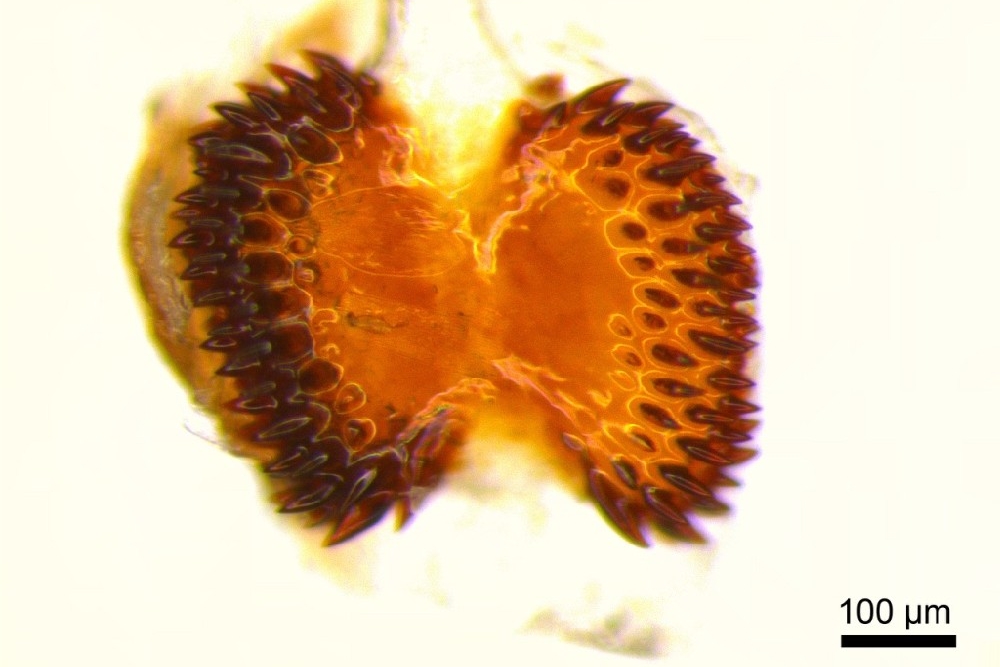

















Further reading
Introduction
Blackiston DJ, Silva Casey E, Weiss MR. Retention of Memory through Metamorphosis: Can a Moth Remember What It Learned As a Caterpillar? PLoS One [Internet]. 2008 Mar 5 [cited 2020 Dec 8];3(3). Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2248710/
Chen P-J, Awata H, Matsushita A, Yang E-C, Arikawa K. Extreme Spectral Richness in the Eye of the Common Bluebottle Butterfly, Graphium sarpedon. Front Ecol Evol [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2020 Dec 8];4. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fevo.2016.00018/full
Diakova AV, Makarova AA, Polilov AA. Between extreme simplification and ideal optimization: antennal sensilla morphology of miniaturized Megaphragma wasps (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). PeerJ [Internet]. 2018 Nov 30 [cited 2020 Dec 8];6. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6276593/
Faisal AA, White JA, Laughlin SB. Ion-Channel Noise Places Limits on the Miniaturization of the Brain’s Wiring. Current Biology. 2005 Jun 21;15(12):1143–9.
Gadenne C, Barrozo RB, Anton S. Plasticity in Insect Olfaction: To Smell or Not to Smell? Annual Review of Entomology. 2016;61(1):317–33.
Giribet G, Edgecombe GD. The Phylogeny and Evolutionary History of Arthropods. Current Biology. 2019 Jun 17;29(12):R592–602.
Göpfert MC, Hennig RM. Hearing in Insects. Annual Review of Entomology. 2016;61(1):257–76.
Hansson BS, Stensmyr MC. Evolution of Insect Olfaction. Neuron. 2011 Dec 8;72(5):698–711.
Hall MJR, Martín-Vega D. Visualization of insect metamorphosis. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2019 Oct 14;374(1783):20190071.
Hustert R. Giant and dwarf axons in a miniature insect, Encarsia formosa, (Hymenoptera, Calcididae). Arthropod Structure & Development. 2012 Nov 1;41(6):535–43.
Juusola M, Dau A, Song Z, Solanki N, Rien D, Jaciuch D, et al. Microsaccadic sampling of moving image information provides Drosophila hyperacute vision. Rieke F, editor. eLife. 2017 Sep 5;6:e26117.
Kawahara AY, Plotkin D, Espeland M, Meusemann K, Toussaint EFA, Donath A, et al. Phylogenomics reveals the evolutionary timing and pattern of butterflies and moths. PNAS. 2019 Nov 5;116(45):22657–63.
Iwamoto H. Structure, function and evolution of insect flight muscle. Biophysics (Nagoya-shi). 2011 Feb 17;7:21–8.
Misof B, Liu S, Meusemann K, Peters RS, Donath A, Mayer C, et al. Phylogenomics resolves the timing and pattern of insect evolution. Science. 2014 Nov 7;346(6210):763–7.
Niven JE, Farris SM. Miniaturization of Nervous Systems and Neurons. Current Biology. 2012 May 8;22(9):R323–9.
Polilov AA. Anatomy of adult Megaphragma (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae), one of the smallest insects, and new insight into insect miniaturization. PLoS One [Internet]. 2017 May 3 [cited 2020 Dec 8];12(5). Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5414980/
Polilov AA. Consequences of miniaturization in insect morphology. Moscow Univ BiolSci Bull. 2015 Jul 1;70(3):136–42.
Regier JC, Shultz JW, Zwick A, Hussey A, Ball B, Wetzer R, et al. Arthropod relationships revealed by phylogenomic analysis of nuclear protein-coding sequences. Nature. 2010 Feb;463(7284):1079–83.
Robert D, Miles RN, Hoy RR. Directional hearing by mechanical coupling in the parasitoid fly Ormia ochracea. J Comp Physiol A. 1996 Jul 1;179(1):29–44.
Sane SP. The aerodynamics of insect flight. Journal of Experimental Biology. 2003 Dec 1;206(23):4191–208.
Truman JW, Riddiford LM. The evolution of insect metamorphosis: a developmental and endocrine view. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2019 Oct 14;374(1783):20190070.
Tuthill JC, Wilson RI. Mechanosensation and adaptive motor control in insects. Curr Biol. 2016 Oct 24;26(20):R1022–38.
Warrant EJ. The remarkable visual capacities of nocturnal insects: vision at the limits with small eyes and tiny brains. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2017 Apr 5;372(1717):20160063.
Chapter 1
Alcock J, Gwynne DT. Courtship Feeding and Mate Choice in Thynnine Wasps (Hymenoptera, Tiphiidae). Aust J Zool. 1987;35(5):451–8.
Alcock J, Forsyth A. Post-copulatory aggression toward their mates by males of the rove beetle Leistotrophus versicolor (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae). Behav Ecol Sociobiol. 1988 May 1;22(5):303–8.
Arnqvist G, Jones TM, Elgar MA. Reversal of sex roles in nuptial feeding. Nature. 2003 Jul;424(6947):387–387.
Avila FW, Sirot LK, LaFlamme BA, Rubinstein CD, Wolfner MF. Insect Seminal Fluid Proteins: Identification and Function. Annu Rev Entomol. 2011;56:21–40.
Bennet-Clark HC. Insect sound production: transduction mechanisms and impedance matching. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1995;49:199–218. Cook J. Figs and fig wasps: Quick Guide. Current Biology. 15(24):978–80.
Córdoba‐Aguilar A, Uhía E, Rivera AC. Sperm competition in Odonata (Insecta): the evolution of female sperm storage and rivals’ sperm displacement. Journal of Zoology. 2003;261(4):381–98.
Forsyth A, Alcock J. Female mimicry and resource defense polygyny by males of a tropical rove beetle, Leistotrophus versicolor (Coleoptera : Staphylinidae). Behav Ecol Sociobiol. 1990 May 1;26(5):325–30.
Goldberg J, Bresseel J, Constant J, Kneubühler B, Leubner F, Michalik P, et al. Extreme convergence in egg-laying strategy across insect orders. Scientific Reports. 2015 Jan 16;5(1):7825.
González A, Rossini C, Eisner M, Eisner T. Sexually transmitted chemical defense in a moth (Utetheisa ornatrix). PNAS. 1999 May 11;96(10):5570–4.
Gwynne DT. Sexual Difference Theory: Mormon Crickets Show Role Reversal in Mate Choice. Science. 1981 Aug 14;213(4509):779–80.
Gwynne DT. Sexual Conflict over Nuptial Gifts in Insects. Annu Rev Entomol. 2007 Dec 7;53(1):83–101.
Lewis SM, Cratsley CK. Flash Signal Evolution, Mate Choice, and Predation in Fireflies. Annu Rev Entomol. 2007 Dec 7;53(1):293–321.
Lückmann J, Assmann T. Reproductive biology and strategies of nine meloid beetles from Central Europe (Coleoptera: Meloidae). Journal of Natural History. 2006 Feb 1;39(48):4101–25.
Meslin C, Cherwin TS, Plakke MS, Hill J, Small BS, Goetz BJ, et al. Structural complexity and molecular heterogeneity of a butterfly ejaculate reflect a complex history of selection. PNAS. 2017 Jul 3;114(27):E5406–13.
Murray RL, Herridge EJ, Ness RW, Wiberg RAW, Bussière LF. Competition for access to mates predicts female-specific ornamentation and male investment in relative testis size. Evolution. 2020;74(8):1741–54.
Normark B. Micromalthus debilis: Quick Guide. Current Biology. 23(10):430–1.
Perotti MA, Young DK, Braig HR. The ghost sex-life of the paedogenetic beetle Micromalthus debilis. Scientific Reports. 2016 Jun 7;6(1):27364.
Plakke MS, Deutsch AB, Meslin C, Clark NL, Morehouse NI. Dynamic digestive physiology of a female reproductive organ in a polyandrous butterfly. Journal of Experimental Biology. 2015 May 15;218(10):1548–55.
Pollock DA, Normark BB. The life cycle of Micromalthus debilisLeConte (1878) (Coleoptera: Archostemata: Micromalthidae): historical review and evolutionary perspective. Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research. 2002;40(2):105–12.
Staab M, Ohl M, Zhu C-D, Klein A-M. A Unique Nest-Protection Strategy in a New Species of Spider Wasp. PLOS ONE. 2014 Jul 2;9(7):e101592.
Sueur J, Mackie D, Windmill JFC. So Small, So Loud: Extremely High Sound Pressure Level from a Pygmy Aquatic Insect (Corixidae, Micronectinae). PLoS One [Internet]. 2011 Jun 15 [cited 2020 Dec 10];6(6). Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3115974/Weiblen GD. How to be a Fig Wasp. Annu Rev Entomol. 2002 Jan 1;47(1):299–330.
Yoshizawa K, Ferreira RL, Kamimura Y, Lienhard C. Female Penis, Male Vagina, and Their Correlated Evolution in a Cave Insect. Current Biology. 2014 May 5;24(9):1006–10.
Yoshizawa K, Ferreira RL, Lienhard C, Kamimura Y. Why Did a Female Penis Evolve in a Small Group of Cave Insects? BioEssays. 2019;41(6):1900005.
Chapter 2
Berendes D, Yang P, Lai A, Hu D, Brown J. Estimation of global recoverable human and animal faecal biomass. Nature Sustainability. 2018 Nov 1;1.
Davis DR, Quintero DA, Cambra RAT, Aiello A. Biology of a New Panamanian Bagworm Moth (Lepidoptera: Psychidae) with Predatory Larvae, and Eggs Individually Wrapped in Setal Cases. Annals of the Entomological Society of America. 2008 Jul 1;101(4):689–702.
Forsyth A, Alcock J. Ambushing and prey-luring as alternative foraging tactics of the fly-catching rove beetleLeistotrophus versicolor (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae). J Insect Behav. 1990 Nov 1;3(6):703–18.
Forti LC, Rinaldi IMP, Camargo R da S, Fujihara RT. Predatory Behavior of Canthon virens (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae): A Predator of Leafcutter Ants [Internet]. Psyche. 2012 [cited 2020 Dec 8]. Available from: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/psyche/2012/921465/
Gwynne DT. Sexual Conflict over Nuptial Gifts in Insects. Annu Rev Entomol. 2007 Dec 7;53(1):83–101.
Johnson JB, Hagen KS. A neuropterous larva uses an allomone to attack termites. Nature. 1981 Feb;289(5797):506–7.
Lüpold S, Manier MK, Puniamoorthy N, Schoff C, Starmer WT, Luepold SHB, et al. How sexual selection can drive the evolution of costly sperm ornamentation. Nature. 2016 May;533(7604):535–8.
Matsuo Y. Extreme Eye Projection in the Male Weevil Exechesops leucopis (Coleoptera: Anthribidae): Its Effect on Intrasexual Behavioral Interferences. J Insect Behav. 2005 Jul 1;18(4):465–77.
Nichols E, Spector S, Louzada J, Larsen T, Amezquita S, Favila ME. Ecological functions and ecosystem services provided by Scarabaeinae dung beetles. Biological Conservation. 2008 Jun 1;141(6):1461–74.
Proctor HC. Indirect Sperm Transfer in Arthropods: Behavioral and Evolutionary Trends. Annual Review of Entomology. 1998;43(1):153–74.
Vahed K. The function of nuptial feeding in insects: a review of empirical studies. Biological Reviews. 1998 Feb;73(1):43–78.
Yoshitake H, Kawashima I. Sexual Dimorphism and Agonistic Behavior of Exechesops Leucopis (Jordan) (Coleoptera: Anthribidae: Anthribinae). cole. 2004 Mar;58(1):77–83.
Chapter 3
Caro T, Ruxton G. Aposematism: Unpacking the Defences. Trends Ecol Evol. 2019 Jul;34(7):595–604.
Conner WE. Adaptive Sounds and Silences: Acoustic Anti-Predator Strategies in Insects. In: Hedwig B, editor. Insect Hearing and Acoustic Communication [Internet]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 2014 [cited 2020 Dec 8]. p. 65–79. (Animal Signals and Communication). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-40462-7_5
Corcoran AJ, Barber JR, Conner WE. Tiger Moth Jams Bat Sonar. Science. 2009 Jul 17;325(5938):325–7.
Dettner K, Liepert C. Chemical Mimicry and Camouflage. Annual Review of Entomology. 1994;39(1):129–54.
Lang C, Seifert K, Dettner K. Skimming behaviour and spreading potential of Stenus species and Dianous coerulescens (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae). Naturwissenschaften. 2012 Nov 1;99(11):937–47.
Skuhrovec J, Stejskal R, Trnka F, Giulio A di. Velcro-Like System Used to Fix a Protective Faecal Shield on Weevil Larvae. PLOS ONE. 2017 Jan 26;12(1):e0170800.
Strohm E, Kroiss J, Herzner G, Laurien-Kehnen C, Boland W, Schreier P, et al. A cuckoo in wolves’ clothing? Chemical mimicry in a specialized cuckoo wasp of the European beewolf (Hymenoptera, Chrysididae and Crabronidae). Front Zool. 2008 Jan 11;5:2.
Sugiura S, Sato T. Successful escape of bombardier beetles from predator digestive systems. Biol Lett. 2018;14(2).
Walker AA, Robinson SD, Yeates DK, Jin J, Baumann K, Dobson J, et al. Entomo-venomics: The evolution, biology and biochemistry of insect venoms. Toxicon. 2018 Nov 1;154:15–27.
Wilson JS, Sidwell JS, Forister ML, Williams KA, Pitts JP. Thistledown velvet ants in the Desert Mimicry Ring and the evolution of white coloration: Müllerian mimicry, camouflage and thermal ecology. Biology Letters. 2020 Jul 29;16(7):20200242.
Chapter 4
Berens AJ, Hunt JH, Toth AL. Comparative transcriptomics of convergent evolution: different genes but conserved pathways underlie caste phenotypes across lineages of eusocial insects. Mol Biol Evol. 2015 Mar;32(3):690–703.
Brune A, Dietrich C. The Gut Microbiota of Termites: Digesting the Diversity in the Light of Ecology and Evolution. Annual Review of Microbiology. 2015;69(1):145–66.
Canciani M, Arnellos A, Moreno A. Revising the Superorganism: An Organizational Approach to Complex Eusociality. Front Psychol [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2020 Dec 8];10. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02653/full
Costa AN, Vasconcelos HL, Vieira-Neto EHM, Bruna EM. Do herbivores exert top-down effects in Neotropical savannas? Estimates of biomass consumption by leaf-cutter ants. vegs. 2008 May;19(6):849–54.
Delaplane KS. Emergent Properties in the Honey Bee Superorganism. Bee World. 2017 Jan 2;94(1):8–15.
Gordon DM. The organization of work in social insect colonies. Complex. 2002 Sep 1;8(1):43–46.
Herz H, Beyschlag W, Hölldobler B. Assessing Herbivory Rates of Leaf-Cutting Ant (Atta colombica) Colonies Through Short-Term Refuse Deposition Counts. Biotropica. 2007;39(4):476–81.
Keller L. Queen lifespan and colony characteristics in ants and termites. Insectes soc. 1998 Aug 1;45(3):235–46.
Korb J. Termites, hemimetabolous diploid white ants? Frontiers in Zoology. 2008 Sep 29;5(1):15.
Masuko K. Larval hemolymph feeding: a nondestructive parental cannibalism in the primitive ant Amblyopone silvestrii Wheeler (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Behav Ecol Sociobiol. 1986 Sep 1;19(4):249–55.
Nowak MA, Tarnita CE, Wilson EO. The Evolution of Eusociality. Nature. 2010 Aug 26;466(7310):1057–62.
Opachaloemphan C, Yan H, Leibholz A, Desplan C, Reinberg D. Recent Advances in Behavioral (Epi)Genetics in Eusocial Insects. Annu Rev Genet. 2018 23;52:489–510.
Parmentier T. Guests of social insects. In 2020.
Pierce N E, Kronauer D J. Myrmecophiles: Quick Guide. Current Biology. 2011;21(6):1–2.
Prestwich GD. Defense Mechanisms of Termites. Annual Review of Entomology. 1984;29(1):201–32.
Sasaki T, Pratt SC. The Psychology of Superorganisms: Collective Decision Making by Insect Societies. Annual Review of Entomology. 2018;63(1):259–75.
Šobotník J, Jirošová A, Hanus R. Chemical warfare in termites. Journal of Insect Physiology. 2010 Sep 1;56(9):1012–21.
Stern DL, Foster WA. The Evolution of Soldiers in Aphids. Biological Reviews. 1996;71(1):27–79.
Styrsky JD, Eubanks MD. Ecological consequences of interactions between ants and honeydew-producing insects. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2007 Jan 22;274(1607):151–64.
Toth AL, Rehan SM. Molecular Evolution of Insect Sociality: An Eco-Evo-Devo Perspective. Annual Review of Entomology. 2017;62(1):419–42.
Way MJ. Mutualism Between Ants and Honeydew-Producing Homoptera. Annual Review of Entomology. 1963;8(1):307–44.
Wilson EO, Hölldobler B. Eusociality: Origin and consequences. PNAS. 2005 Sep 20;102(38):13367–71.
Chapter 5
Ashe J, Timm R. Systematics, distribution, and host specificity of Amblyopinus Solsky 1875 (Coleoptera Staphylinidae) in Mexico and Central America. Tropical Zoology. 1995 Nov 1;8.
Broad GR, Quicke DL. The adaptive significance of host location by vibrational sounding in parasitoid wasps. Proc Biol Sci. 2000 Dec 7;267(1460):2403–9.
Carton Y, Poirié M, Nappi AJ. Insect immune resistance to parasitoids. Insect Science. 2008;15(1):67–87.
Eggleton P, Belshaw R. Insect parasitoids: an evolutionary overview. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B: Biological Sciences. 1992 Jul 29;337(1279):1–20.
Fatouros NE, Cusumano A, Bin F, Polaszek A, van Lenteren JC. How to escape from insect egg parasitoids: a review of potential factors explaining parasitoid absence across the Insecta. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2020 Jul 29;287(1931):20200344.
Malfi RL, Davis SE, Roulston TH. Parasitoid fly induces manipulative grave-digging behaviour differentially across its bumblebee hosts. Animal Behaviour. 2014 Jun 1;92:213–20.
Wells A. The first parasitic Trichoptera. Ecological Entomology. 1992;17(3):299–302.
